Last Updated on November 25, 2022 by mdmtool
Generators and alternators are two common types of electrical equipment used to generate electricity. Though both perform the same primary function, there are some important differences between them.
What Is An Alternator?
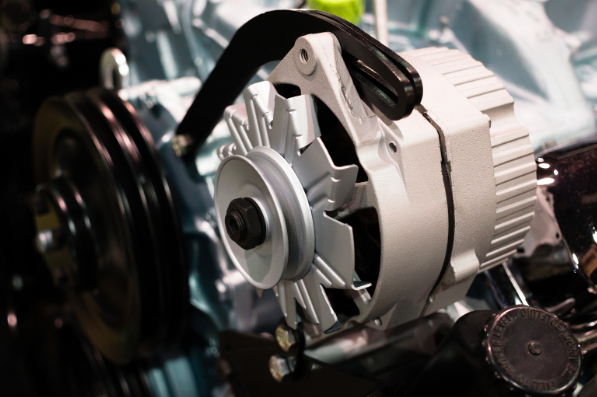
An alternator is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy into alternating current (AC) electrical energy. It is a type of AC generator. Alternators are used in various applications, including vehicles, as a part of the charging system.
What Is A Generator?

A generator is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The reverse would be converting electrical power into mechanical energy by an electric motor. Generators are used in various applications, from small portable units to large industrial machines.
Differences Between Alternator And Generator
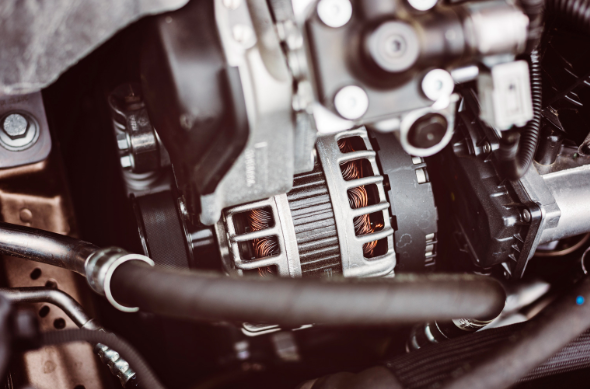
- Current: The alternator produces AC while the generator produces DC.
- Coil winding direction: The winding direction of the coil in an alternator is opposite to that of a generator.
- Efficiency: Alternators are more efficient than generators. Alternators and generators are two types of electrical machines used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The main difference between an alternator and a generator is that the alternator converts mechanical energy into the alternating current while the generator converts mechanical energy into direct current.
- Voltage: The voltage produced by an alternator is more than a generator. The reason is that, in an alternator, the flux is constant while the armature rotates. In contrast, in a generator, the armature is stationary, and the change produced by the field winding is turning.
- AC machines: An alternator is an ac machine, while the generator can be either an ac or a dc machine. An alternator is an electrical machine that converts mechanical energy into alternating current (AC). The main component of an alternator is a rotating magnetic field called the rotor. The rotor is connected to the prime mover, which supplies the rotational energy. The stator is the alternator’s stationary part, consisting of windings. The rotating magnetic field of the rotor induces a voltage in the stator windings. This induced voltage is used to generate AC.
- DC Machines: A generator is an electrical machine that converts mechanical energy into direct current (DC). The main component of a generator is a rotating armature winding called field winding. The armature is connected to the prime mover, which supplies the rotational energy. The stator is the generator’s stationary part, consisting of windings. The rotating armature winding of the generator produces a voltage in the stator windings. This induced voltage is used to generate DC.
- Applications: Alternators are used in power plants to generate electricity. They are also used in cars and trucks to charge the battery. Generators are used in emergency power systems to provide power during power outages.
- Power System: The main difference between a generator and an alternator is that a generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, while an alternator converts chemical energy into electrical energy. Generators are classified into direct current (DC) generators and alternating current (AC) generators.
How An Alternator Works?
An alternator uses a spinning magnet (the rotor) to produce an electric current in the stator, a stationary set of coils. The rotating magnet creates a magnetic field that induces a current in the stator coils. This current is then converted into AC power by the rectifier bridge.
How Does A Generator Work?
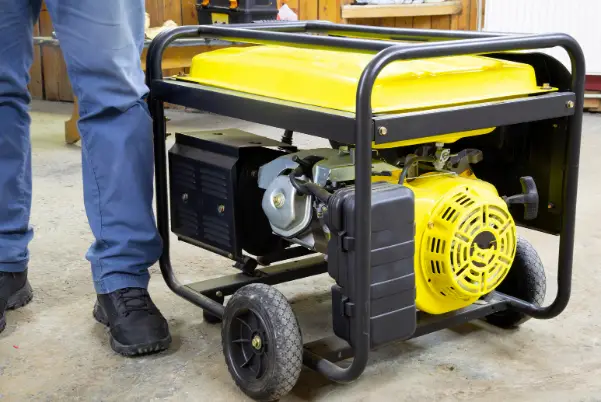

A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. This conversion is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The working of a generator is very simple. It consists of a rotating coil of wire called the armature, and a stationary magnet called the stator. When the armature coil rotates, it cuts through the stator’s magnetic field, which induces a voltage in the coil. This induced voltage causes a current to flow in the coil and this, in turn, produces electricity.
DC And AC Electricity
AC electricity: AC electricity is produced by an alternator. Alternators work by using magnets to produce an electric current. The electricity produced by an alternator is alternating current (AC). This means that the direction of the current reverses periodically. AC electricity is used in most homes and businesses in the United States.
DC electricity: DC electricity is produced by a generator. Generators work by using magnets to create an electric current. The electricity produced by a generator is direct current (DC). This means that the direction of the current does not reverse. DC electricity is used in some homes and businesses but is not as common as AC electricity.
FAQs
How much electricity can alternator produce?
It can produce power up to 25000 watt.
Conclusion
The main difference between a generator and an alternator is that a generator uses mechanical energy to produce electricity, whereas an alternator uses electromagnetic induction. Generators are primarily used in portable applications such as camping or emergencies, while alternators are widely used in automobiles.





